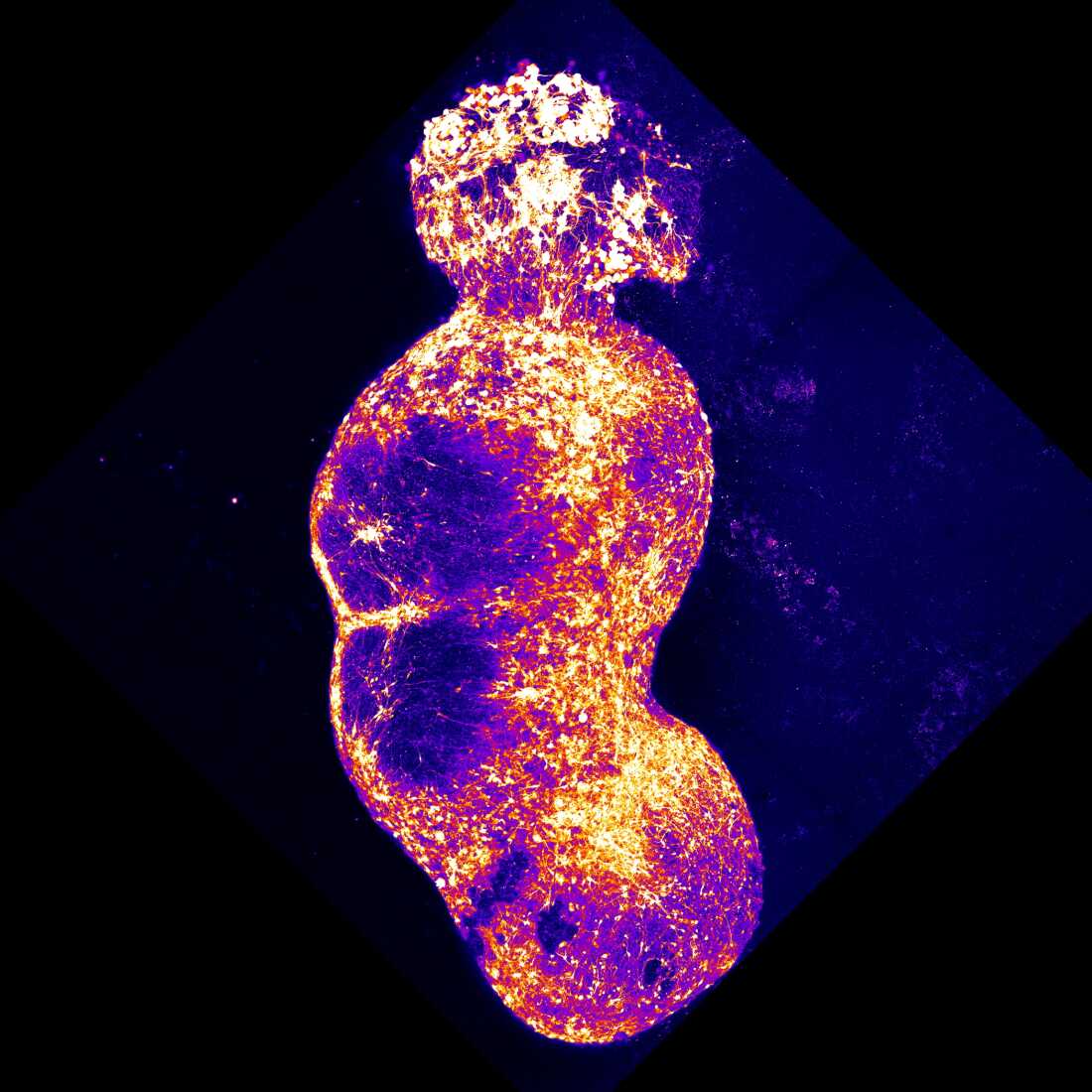
Researchers built-in 4 organoids that symbolize the 4 parts of the human sensory pathway, alongside which ache indicators are conveyed to the mind. Stimulation of the sensory organoid (high) by substances, resembling capsaicin, triggers neuronal exercise that’s then transmitted all through the remainder of the organoids.
Pasca lab/Stanford Drugs
conceal caption
toggle caption
Pasca lab/Stanford Drugs
Scientists have re-created a ache pathway within the mind by rising 4 key clusters of human nerve cells in a dish.
This laboratory mannequin might be used to assist clarify sure ache syndromes, and supply a brand new technique to check potential analgesic medication, a Stanford workforce stories within the journal Nature.
“It is thrilling,” says Dr. Stephen Waxman, a professor at Yale College of Drugs who was not concerned within the analysis.
At the moment, potential ache medication are sometimes examined in animals — whose responses are sometimes completely different than a human’s — and in particular person nerve cells, which can not replicate the conduct of whole mind networks.
With this new system, often called a mind assembloid, “we now have a miniature nervous system that is perhaps a really helpful platform,” Waxman says.
A pathway with a number of stops
The mannequin is the results of an effort to re-create the signaling chain that happens after publicity to painful stimuli, says Dr. Sergiu Pașca, a professor at Stanford College who led the undertaking.
Contact a sizzling range, for instance, and particular cells within the pores and skin “ship that info all the best way to the spinal wire,” Pașca says. “Then the spinal wire will relay it as much as the thalamus deep within the mind, after which all the best way to the outer layer of the mind, which is the cortex.”
To approximate this pathway within the lab, Pașca’s workforce created 4 completely different mind organoids, spherical clumps of human nerve cells that develop in a dish. The workforce coaxed every organoid to resemble one particular sort of mind or spinal tissue discovered alongside the ache pathway.
“After which we put them collectively, actually put them in shut proximity, and watched them as they linked with one another,” Pașca says.
After greater than six months creating within the lab, the ensuing assembloid had created a pathway linking the 4 organoids. The nerve cells additionally spontaneously started “working in a coordinated style throughout the 4 elements of this assembloid,” Pașca says.
Chili peppers and ache syndromes
To check the mannequin, the workforce uncovered it to capsaicin, the chemical that makes chili peppers painfully sizzling.
“Then you definitely begin seeing that info touring,” Pașca says. “The neurons that sense these indicators get activated and so they transmit that info to the following station and the following station, all the best way to the cortex.”
Subsequent, the scientists tried creating assembloids utilizing cells with genetic variants linked to irregular ache notion.
Considered one of these variants causes a uncommon situation referred to as erythromelalgia, or man-on-fire syndrome.
“These people really feel searing, burning, scalding ache in response to delicate heat,” Waxman says.
The scientists discovered that assembloids with the gene variant produced rather more spontaneous communication between organoids, suggesting a heightened sensitivity to ache.
Outcomes like that recommend that organoids are already a helpful technique to examine each nervous system ailments and the pathways they have an effect on, says Dr. Guo-li Ming, a professor on the College of Pennsylvania’s Perelman College of Drugs who additionally had no function within the new examine.
For all its complexity, the ache pathway in a dish is a extremely simplified model of what goes on in an individual, Ming provides. For instance, people have two main pathways that carry ache indicators to the mind, whereas the mannequin system consists of only one.
Consequently, the mannequin can detect a painful stimulus, however does not produce an emotional response, Pasca says.
“So we do not consider that this pathway that we have constructed is in any means feeling ache,” he says.
And these clusters of human cells are prone to develop into much more useful as scientists discover methods to re-create bigger and extra advanced elements of the nervous system.
For instance, Ming’s personal lab has developed a mannequin of a human neural tube, the construction in an embryo that finally turns into right into a child’s mind and spinal wire. Her purpose is to grasp how neurological problems develop early in life.


